Fruit fly study reveals brain-cell circuitry that could underlie how creatures large and small see wavelengths of light


Perceiving something—anything—in your surroundings is to become aware of what your senses are detecting. Now, Columbia University neuroscientists have identified, for the first time, brain-cell circuitry in fruit flies that converts raw sensory signals into color perceptions that can guide behavior.
Their findings are published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
“Many of us take for granted the rich colors we see every day—the red of a ripe strawberry or the deep brown in a child’s eyes. But those colors do not exist outside of our brains,” said Rudy Behnia, Ph.D., a principal investigator at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute and the corresponding author on the paper. Rather, she explained, colors are perceptions the brain constructs as it makes sense of the longer and shorter wavelengths of light detected by the eyes.
“Turning sensory signals into perceptions about the world is how the brain helps organisms survive and thrive,” Dr. Behnia said.
“To ask how we perceive the world seems like a simple question, but answering it is a challenge,” added Dr. Behnia. “My hope is that our efforts to uncover neural principles underlying color perception will help us better understand how brains extract the features in the environment that are important for making it through each day.”
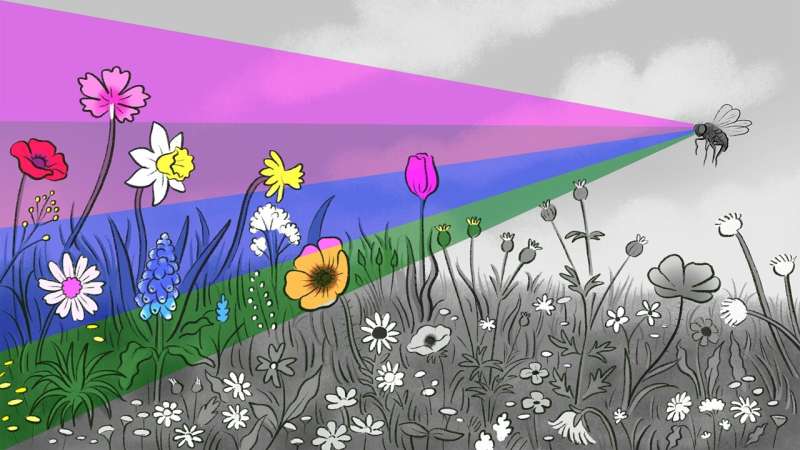
In their new paper, the research team reports discovering specific networks of neurons, a type of brain cell, in fruit flies that respond selectively to various hues. Hue denotes the perceived colors associated with specific wavelengths, or combinations of wavelengths of light, which themselves are not inherently colorful. These hue-selective neurons lie within the optic lobe, the brain area responsible for vision.
Among the hues these neurons respond to are those that people would perceive as violet and others that correspond to ultraviolet wavelengths (not detectable by humans). Detecting UV hues is important for the survival of some creatures, such as bees and perhaps fruit flies; many plants, for example, possess ultraviolet patterns that can help guide insects to pollen.
Scientists had previously reported finding neurons in animals’ brains that respond selectively to different colors or hues, say, red or green. But no one had been able to trace the neural mechanisms making this hue selectivity possible.
This is where the recent availability of a fly-brain connectome has proven helpful. This intricate map details how some 130,000 neurons and 50 million synapses in a fruit-fly’s poppy seed-sized brain are interconnected, said Dr. Behnia, who is also an assistant professor of neuroscience at Columbia’s Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
With the connectome serving as a reference—akin to a picture on a puzzle box serving as a guide for how a thousand pieces fit together—the researchers used their observations of brain cells to develop a diagram they suspected represents the neuronal circuitry behind hue selectivity. The scientists then portrayed these circuits as mathematical models to simulate and probe the circuits’ activities and capabilities.
“The mathematical models serve as tools that enable us to better understand something as messy and complex as all of these brain cells and their interconnections,” said Matthias Christenson, Ph.D., a co-first author on the paper and a former member of Dr. Behnia’s lab. “With the models, we can work to make sense of all of this complexity.”
Also contributing crucially to the modeling work was Dr. Larry Abbott, William Bloor Professor of Theoretical Neuroscience, Professor of Physiology and Cellular Biophysics and a principal investigator at the Zuckerman Institute.
Not only did the modeling reveal that these circuits can host activity required for hue selectivity, it also pointed to a type of cell-to-cell interconnectivity, known as recurrence, without which hue-selectivity cannot happen. In a neural circuitry with recurrence, outputs of the circuit circle back in to become inputs. And that suggested yet another experiment, said Álvaro Sanz-Diez, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in Dr. Behnia’s lab and the other co-first author of the Nature Neuroscience paper.
“When we used a genetic technique to disrupt part of this recurrent connectivity in the brains of fruit flies, the neurons that previously showed hue-selective activity lost that property,” said Dr. Sanz-Diez. “This reinforced our confidence that we really had discovered brain circuitry involved in color perception.”
“Now we know a little more about how the brain’s wiring makes it possible to build a perceptual representation of color,” said Dr. Behnia. “My hope is that our new findings can help explain how brains produce all kinds of perceptions, among them color, sound and taste.”
More information:
Hue selectivity from recurrent circuitry in Drosophila, Nature Neuroscience (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01640-4
Citation:
Fruit fly study reveals brain-cell circuitry that could underlie how creatures large and small see wavelengths of light (2024, May 16)
retrieved 16 May 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-05-fruit-fly-reveals-brain-cell.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.